Mean Value Theorem Conditions Math
The mean value theorem is one of the central theorems of differential calculus.
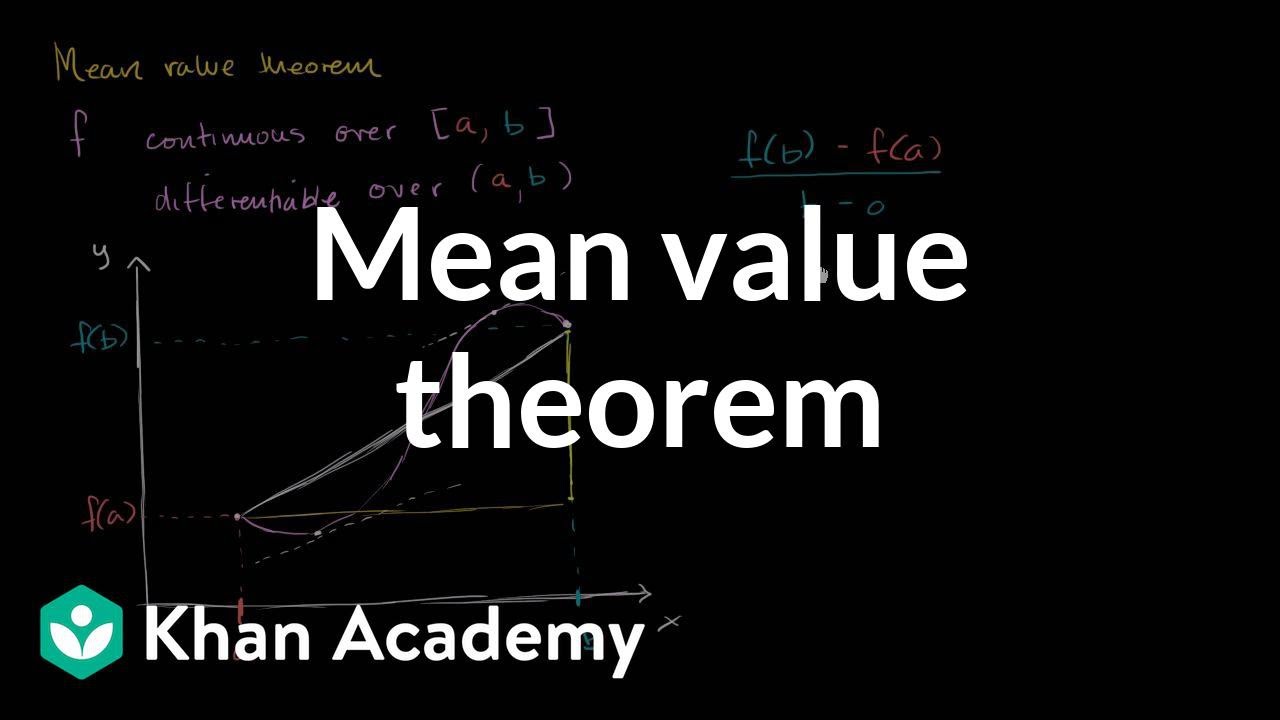
Mean value theorem conditions math. Now for the plain english version. Here s the formal definition of the theorem. It is one of the most important results in real analysis. Thus the mean value theorem links the secant slope with the derivative of a function.
It states roughly speaking that the slope of the secant between two different points of a differentiable function somewhere between these two points is assumed to be a derivative. More precisely the theorem states that if f displaystyle f. In mathematics the mean value theorem states roughly that for a given planar arc between two endpoints there is at least one point at which the tangent to the arc is parallel to the secant through its endpoints. The mean value theorem generalizes rolle s theorem by considering functions that are not necessarily zero at the endpoints.
This theorem is used to prove statements about a function on an interval starting from local hypotheses about derivatives at points of the interval. Anybody can ask a question anybody can answer the best answers are voted up and rise to the top home. The mean value theorem is one of the most important theoretical tools in calculus. It states that if f x is defined and continuous on the interval a b and differentiable on a b then there is at least one number c in the interval a b that is a c b such that the special case when f a f b is known as rolle s theorem.
Mathematics stack exchange is a question and answer site for people studying math at any level and professionals in related fields. Real analysis conditions for the mean value theorem mathematics stack exchange. Mathematics stack exchange is a question and answer site for people studying math at any level and professionals in related fields. The mean value theorem and its meaning rolle s theorem is a special case of the mean value theorem.
Sign up to join this community. Now to find the numbers that satisfy the conclusions of the mean value theorem all we need to do is plug this into the formula given by the mean value theorem. F c f 2 f 1 2 1 3 c 2 4 c 1 14 2 3 12 3 4 f c f 2 f 1 2 1 3 c 2 4 c 1 14 2 3 12 3 4. Ask question asked 5 years.
In rolle s theorem we consider differentiable functions f that are zero at the endpoints. It only takes a minute to sign up. The mean value theorem mvt lagrange s mean value theorem mvt states that if a function f x is continuous on a closed interval a b and differentiable on the open interval a b then there is at least one point x c on this interval such that f b f a f c b a. Anybody can ask a question anybody can answer the best answers are voted up and rise to the top home questions tags users unanswered condition of the mean value theorem.
The mean value theorem which most of us know starts with the conditions that f is continuous on the closed interval a b and differentiable on the opened interval a b then there exists a. The mean value theorem. If f is continuous on the closed interval a b and differentiable on the open interval a b then there exists a number c in a b such that. It only takes a minute to sign up.


























